Canine kidney disease, a prevalent yet often overlooked condition, poses a significant health risk to dogs of all breeds and ages. This article delves into the intricacies of this disease, aiming to provide comprehensive information on its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Understanding this condition is crucial for pet owners, as early detection and proper care can greatly influence the management and outcome of the disease. This exploration serves as a guide to help dog owners recognize signs of kidney disease, understand its implications, and make informed decisions about their pet’s health.
Understanding Canine Kidney Disease
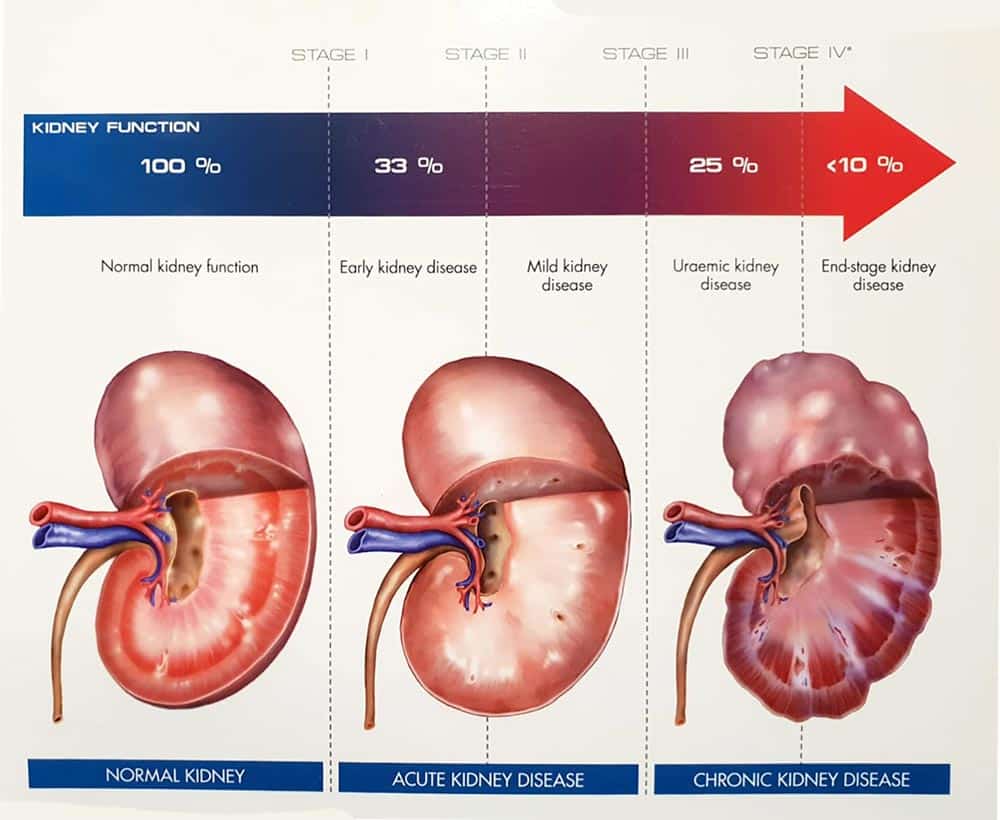
The kidneys play a vital role in a dog’s body, functioning to remove waste products, maintain hydration, and regulate essential minerals. Canine kidney disease disrupts these crucial processes, leading to a buildup of toxins in the body. This disease manifests in two forms: acute kidney disease, which occurs suddenly and is often reversible, and chronic kidney disease, a gradual loss of kidney function over time. Despite common misconceptions, canine kidney disease is not always a death sentence; with proper management, many dogs continue to lead fulfilling lives.
Understanding this ailment is the first step in combating its effects. Misconceptions, such as the belief that it only affects older dogs or that it’s always fatal, can hinder effective care. Educating oneself about the nuances of this disease is essential for timely and appropriate responses to its onset.
Causes of Kidney Disease in Dogs
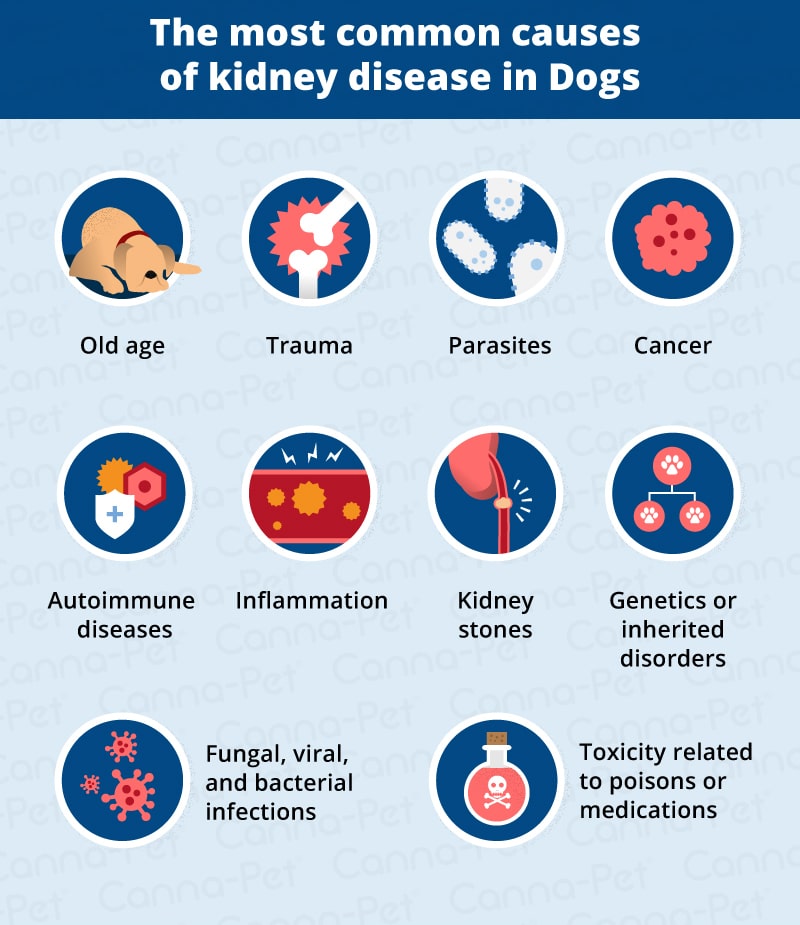
The causes of kidney disease in dogs are diverse, encompassing genetic, environmental, and age-related factors. Certain breeds, like Cocker Spaniels and Bull Terriers, are genetically predisposed to kidney problems, indicating a hereditary element. Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins, harmful diets, or specific medications, can also precipitate kidney disease. Prolonged use of medications like NSAIDs can inadvertently harm kidney function.
Age plays a significant role as well, with older dogs being more susceptible to chronic kidney disease. This doesn’t negate the fact that younger dogs can also be affected, often due to congenital abnormalities or acute injuries. It’s crucial for owners to understand these risk factors to better protect their pets and seek early intervention.
Recognizing the Symptoms
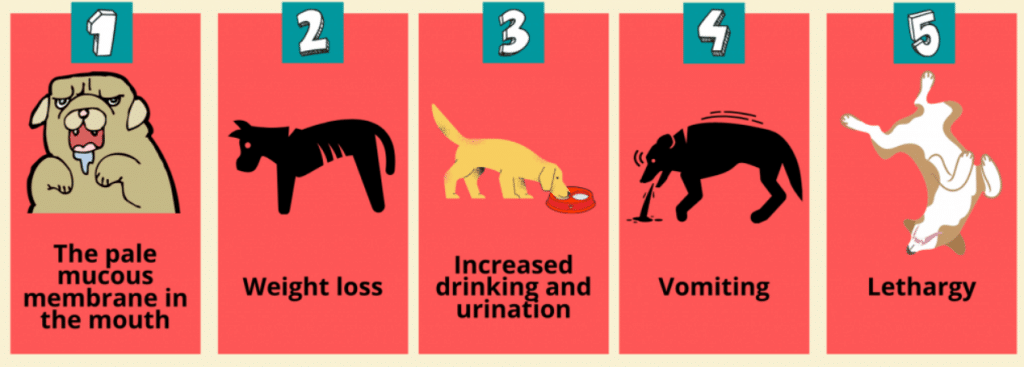
Early detection of kidney disease hinges on recognizing its symptoms. Initial signs are often subtle, such as increased thirst or a change in urination patterns. Dogs may drink more water than usual or have accidents indoors. These early symptoms can easily be overlooked, which is why vigilance is key.
As the disease progresses, more noticeable symptoms emerge. These include weight loss, vomiting, and a noticeable decrease in energy levels. Dogs may exhibit a lack of interest in activities they once enjoyed. Understanding these signs is crucial for early intervention, which can significantly alter the course of the disease and improve a dog’s quality of life.
Diagnosis of Canine Kidney Disease
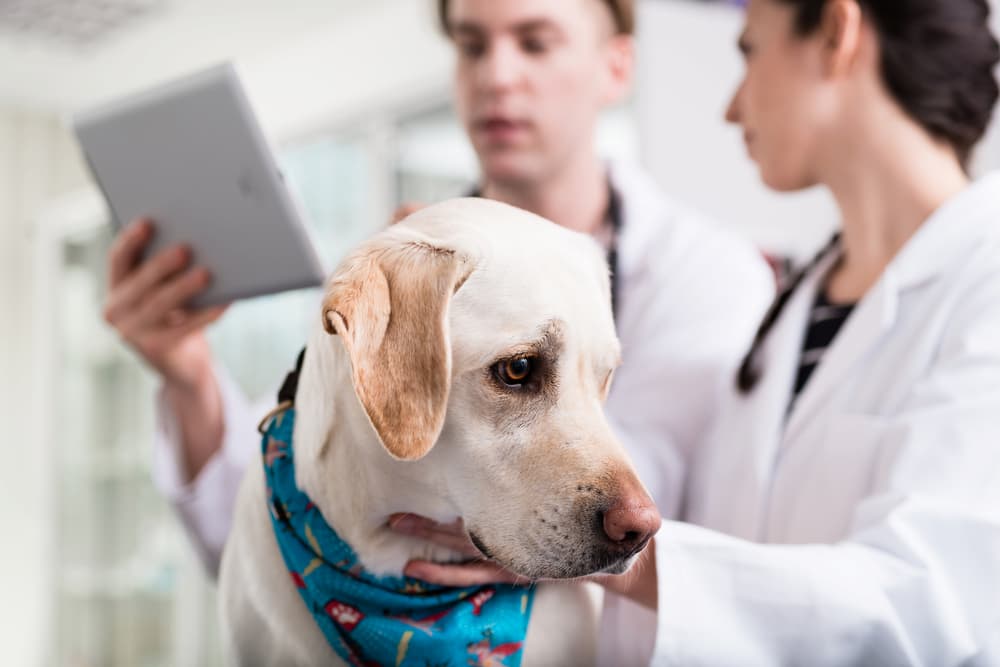

The diagnosis of canine kidney disease is a critical step in managing the condition effectively. Regular veterinary check-ups are essential, especially for breeds prone to kidney issues or older dogs. During these check-ups, a veterinarian will typically perform blood tests and a urine analysis to assess kidney function. Elevated levels of creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in blood tests, along with abnormal findings in urine, such as protein or blood, often indicate kidney problems.
Advanced diagnostic methods may be employed if initial tests suggest kidney disease. These can include ultrasound and X-rays, which help in assessing the shape, size, and structure of the kidneys, revealing abnormalities like kidney stones or tumors. A biopsy may also be recommended in some cases to determine the extent of kidney damage. Understanding the diagnostic process can help pet owners prepare for and participate in their dog’s care journey.
Treatment Options
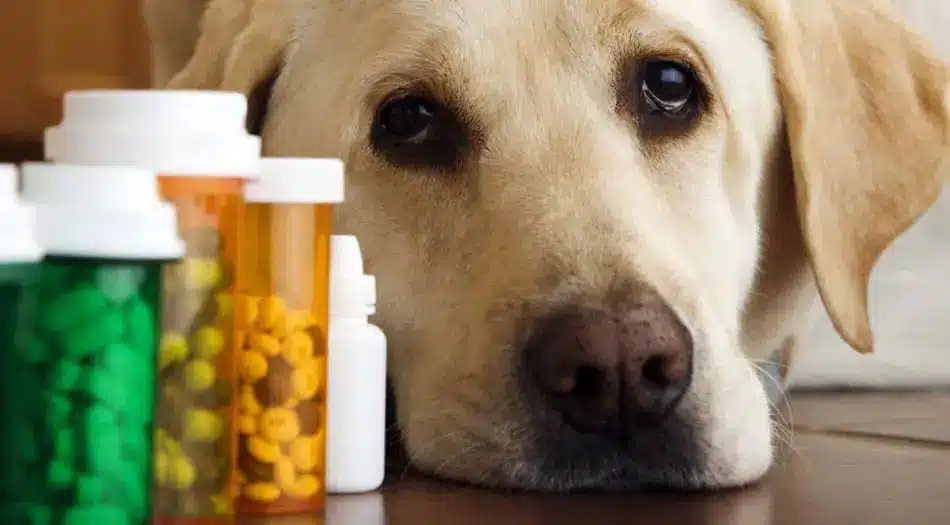

Upon diagnosis, a range of treatment options are available depending on the severity and progression of the kidney disease. Dietary management plays a pivotal role in treatment. Specialized diets, typically low in protein and phosphorus, help reduce the workload on the kidneys, slowing the progression of the disease. Hydration is equally crucial, and vets may recommend methods to encourage water intake or administer subcutaneous fluids.
Medications are often prescribed to manage symptoms such as hypertension or to reduce protein loss in urine. In more advanced cases, treatments like dialysis or even kidney transplants can be considered. While these treatments can be intensive and costly, they offer a chance to extend and improve the quality of a dog’s life. It’s important for pet owners to understand the potential benefits and challenges of each treatment option.
Managing Canine Kidney Disease
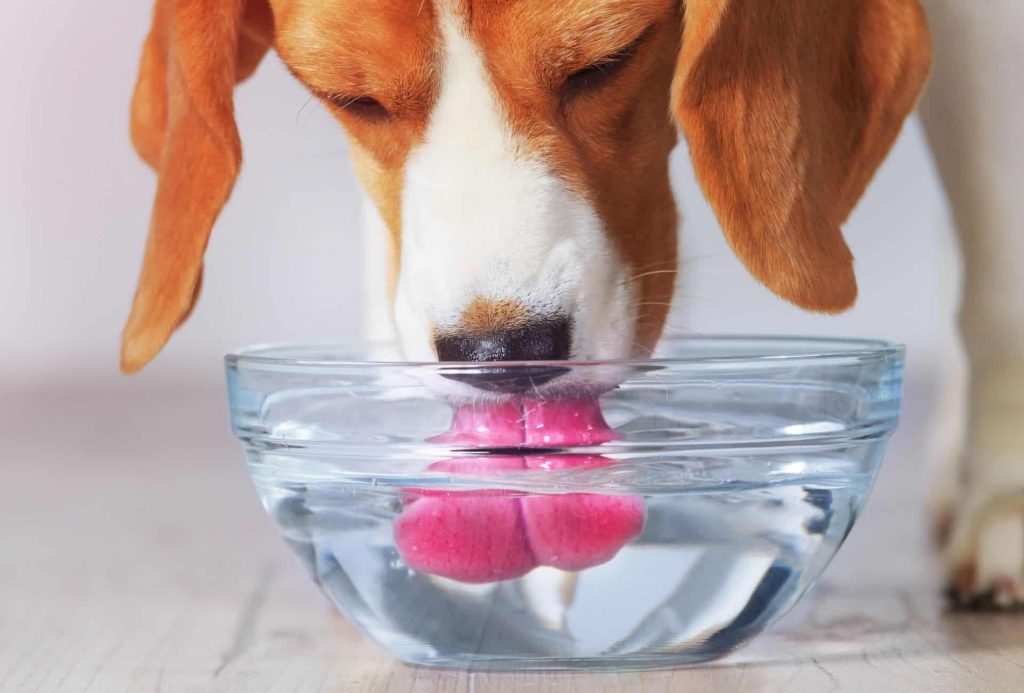

Managing canine kidney disease is a daily commitment that extends beyond medical treatment. Adequate hydration is fundamental, and owners may need to find creative ways to encourage their dogs to drink more water. Adjusting a dog’s diet to meet their specific needs is also crucial. Regular exercise, while ensuring it’s not too strenuous, helps maintain overall health and well-being.
Regular veterinary visits are essential for monitoring the progression of the disease and adjusting treatments as necessary. In addition to medical care, the emotional and comfort needs of the dog should be addressed. Providing a comfortable resting area, maintaining a routine, and offering gentle, supportive care can significantly impact a dog’s quality of life. Owners need to be attuned to their pet’s changing needs and be prepared to make adjustments to their care regimen as the disease progresses.
Prevention Strategies
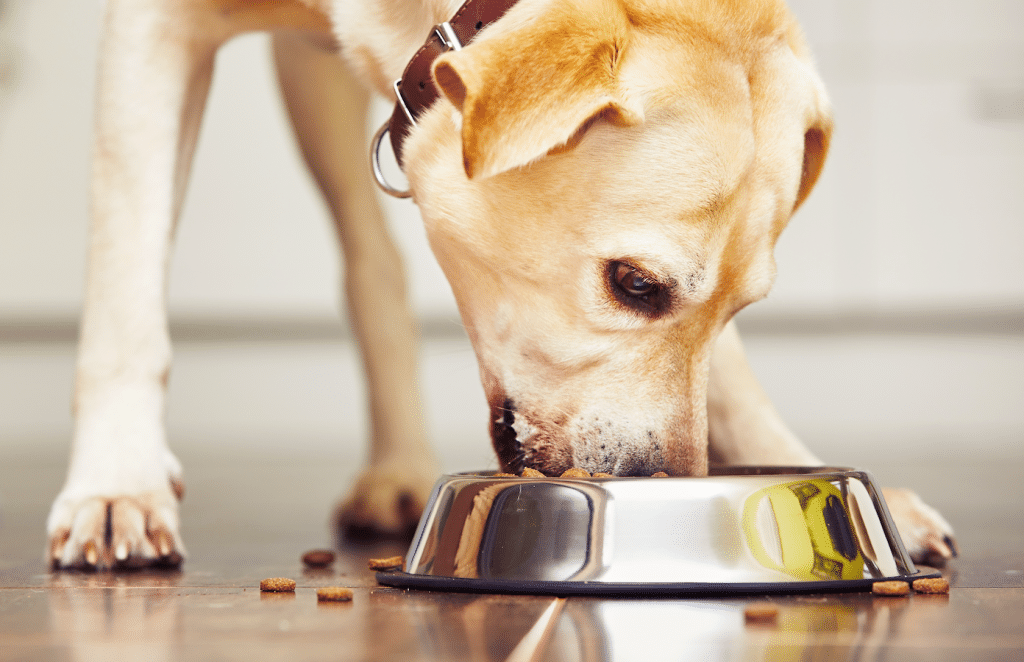

Preventing kidney disease in dogs, where possible, starts with a focus on diet and nutrition. Feeding a balanced diet that is appropriate for the dog’s age, breed, and health status is crucial. Owners should avoid foods that are high in phosphorus and protein, which can strain the kidneys. Additionally, ensuring that dogs have constant access to clean water helps in maintaining kidney health and preventing dehydration, a common factor that exacerbates kidney issues.
Regular health check-ups play a vital role in early detection and prevention of kidney disease. These check-ups allow for early intervention if there are signs of kidney stress or damage. Educating dog owners about the risk factors and signs of kidney disease is also essential. Awareness can lead to earlier detection and treatment, which can significantly improve the outcome for dogs with kidney disease.
Support and Resources for Owners

Dealing with a dog’s kidney disease can be challenging for owners, both emotionally and in terms of care. Finding support through communities and groups, either in person or online, can provide invaluable resources and emotional support. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges can offer practical advice and emotional comfort. Additionally, veterinarians and veterinary nurses are excellent sources of support and information.
Access to online resources, such as educational materials and webinars, can help owners understand and manage their dog’s condition better. These resources often provide insights into the latest research, treatment options, and management strategies. In the advanced stages of kidney disease, owners may need to make difficult decisions regarding palliative care and quality of life. Guidance from veterinary professionals and support groups can be instrumental in navigating these tough choices, ensuring that decisions are made with the dog’s best interests at heart.
Navigating Canine Kidney Disease
Understanding and managing canine kidney disease is a multifaceted journey that requires awareness, early detection, and proactive care. This blog post has highlighted the importance of recognizing the signs, understanding the causes, and exploring the available treatments and management strategies. It’s essential for dog owners to remain vigilant and informed, as their role is crucial in enhancing the quality of life for their pets. By embracing prevention strategies, seeking timely medical intervention, and providing ongoing support, owners can significantly impact the health and well-being of their dogs, navigating the challenges of kidney disease with knowledge and compassion.